Abstract
Background: Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disease (PTLD) occurs following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HCT) as a consequence of immunosuppression. In most cases following HCT, PTLD is associated with Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) infection of B cells, either due to reactivation, or from primary EBV infection (Styczynski J, Haematol. 2016; Allen UD, Am J Transplant, 2019; Nijand M, Transplant Direct, 2016). Clinical practice treatment guidelines recommend rituximab as preemptive therapy for EBV reactivation (based on EBV virus load) and for treatment of EBV-driven (EBV +) PTLD following HCT. However, EBV + PTLD patients (pts) who fail rituximab have very poor outcomes with limited treatment options. There are ongoing clinical studies investigating innovative therapies to address unmet needs in these pts. Published evidence on the clinical outcomes of these pts who fail rituximab is also limited. We aimed to describe the outcomes for pts diagnosed with EBV + PTLD following HCT who fail rituximab in a multinational real-world setting.
Methods: We conducted a large multinational, multicenter retrospective chart review study of EBV + PTLD pts following HCT or solid organ transplantation who received rituximab or rituximab plus chemotherapy (CT) between January 2000-December 2018 and were refractory (failed to achieve complete response [CR] or partial response [PR]) or relapsed at any point after such therapy. Treatment response was assessed by either clinical diagnosis, radiographic/imaging, biopsy/cytology, or a combination of such assessments. Data was collected from 29 centers across North America (United States and Canada) and the European Union. The study population was aligned with the ongoing investigational trial (Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT03394365). This analysis includes pts with EBV + PTLD following HCT who were refractory or relapsed after rituximab ± CT as first line of therapy. The Kaplan-Meier (KM) method was used to estimate the overall survival (OS). Rituximab failure date was defined as the earliest date when pts became refractory or relapsed following rituximab ± CT.
Results: A total of 81 pts with EBV + PTLD following HCT who failed rituximab ± CT were included in the analysis. Median age at PTLD diagnosis was 49 years (interquartile range [IQR]: 33‒57) and median time to PTLD onset from transplant was 3 months (IQR: 1.9‒4.2). Median follow-up time was 1.7 months (IQR: 0.6‒3.4) from the date of PTLD diagnosis. Of all the PTLDs, 52 (64.2%) were monomorphic, 18 (22.2%) polymorphic, 2 (2.5%) early lesions, and 9 (11.1%) were unknown. The most common PTLD subtype was diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (46, 56.8%).
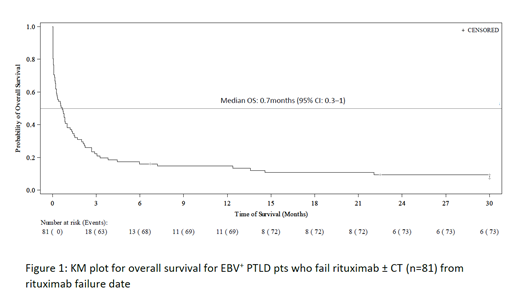
Sixty-eight (84%) pts received rituximab monotherapy and 13 (16%) pts received rituximab plus CT as first line of therapy. Seven out of 13 pts who received rituximab plus CT had received preemptive rituximab treatment for EBV viremia prior to PTLD treatment. Median OS was 0.7 months (95% CI: 0.3‒1; IQR: 0.1‒2.7) for 81 pts who failed first line rituximab ± CT (Figure 1). Median OS from PTLD diagnosis was 1.7 months (95% CI: 1.1‒2.3; IQR: 0.6‒3.4).
Seventy-four (91.4%) out of the 81 pts ultimately died. Causes of death comprised 50 (67.6%) related to PTLD and therapy, 10 (13.5%) graft-versus-host disease (GvHD), 5 (6.8%) from sepsis/infection, 3 (4.1%) due to primary disease leading to HCT, 2 (2.7%) organ failure, 1 (1.4%) graft failure, 1 (1.4%) from hepatic failure, and 2 (2.7%) unknown.
Conclusions: The prognosis of EBV + PTLD pts following HCT who fail rituximab ± CT remains very poor with an estimated median OS of less than 1 month, highlighting the significant unmet need in this population.
Storek: Atara Biotherapeutics: Other: Site PI, Research Funding. Socié: Alexion: Research Funding. Thirumalai: Atara Biotherapeutics: Current Employment. Guzman-Becerra: Atara Biotherapeutics: Current Employment. Xun: Atara Biotherapeutics: Current Employment. Kumar: Roche: Research Funding; GSK: Research Funding; Amplyx: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Takeda & Atara: Research Funding. Sadetsky: Atara Biotherapeutics: Current Employment. Dierickx: Sandoz: Consultancy; Sanofi: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda, Incyte, Atara: Consultancy. Reitan: Atara, Kite, Janssen: Research Funding. Barlev: Atara Biotherapeutics: Current Employment. Mohty: Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Jazz: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal